Difference between revisions of "Reduce Access to Prescription Drugs"
Josiebeets (talk | contribs) |
Josiebeets (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | <div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"> | + | <div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"><div class="mw-parser-output"> |
''Return to [[Opioid_Top-Level_Strategy_Map|Opioid Top-Level Strategy Map]]'' | ''Return to [[Opioid_Top-Level_Strategy_Map|Opioid Top-Level Strategy Map]]'' | ||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
<span style="background-color: #ffffff">[[RTI_-_Reduce_Access_to_Opioids|More RTI on Reducing Access to Opioids]]</span> | <span style="background-color: #ffffff">[[RTI_-_Reduce_Access_to_Opioids|More RTI on Reducing Access to Opioids]]</span> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<div class="mw-parser-output"> | <div class="mw-parser-output"> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
= Sources = | = Sources = | ||
| − | </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> | + | </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> </div> |
[[Category:SAFE-Public Awareness]] | [[Category:SAFE-Public Awareness]] | ||
Revision as of 18:34, 19 November 2019
Return to Opioid Top-Level Strategy Map
One of the reasons that so many people began misusing opioid pain medication is that the drug was so easy to access for use that was appropriate medical use. The intent of this objective is NOT to end access to opioid use for those who are legitimately using the opioids for prescribed use and who understand the risks of that use. The focus of this objecitve is to make opioid pills less accessible to people who would misuse them.
Contents
Background
Access to Opioids for Non-Medical Use (Misuse)
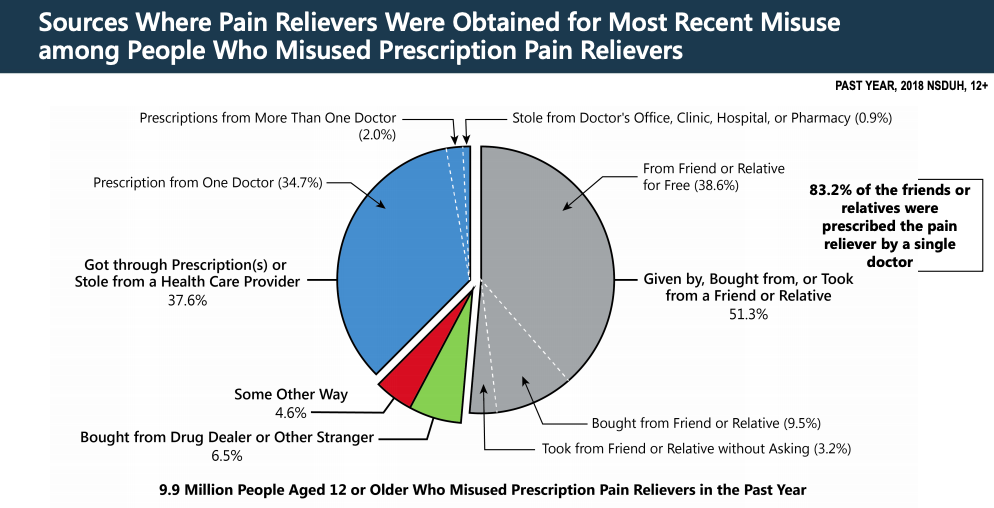
The vast majority of misused prescription opioids come from friends and family of the person misusing through both intentional and unintentional diversion. The annual National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) indicated that more than half of people misusing opioids received their prescription opioids through these methods. Only 6.5% sourced their prescription opioids from a drug dealer.
Source of Graphic: SAMHSA, Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality, National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 2018.
According to the survey (which always is influenced by the sample surveyed and their honesty in answering the survey) indicates that of people who misused pain relievers, the majority (53.1%) responded that they received them from a friend or relative.[1]
- 38.5% received them from a friend or relative for free.
- 10.6% purchased them from a friend or relative
- 4.0% took them from a friend or strange
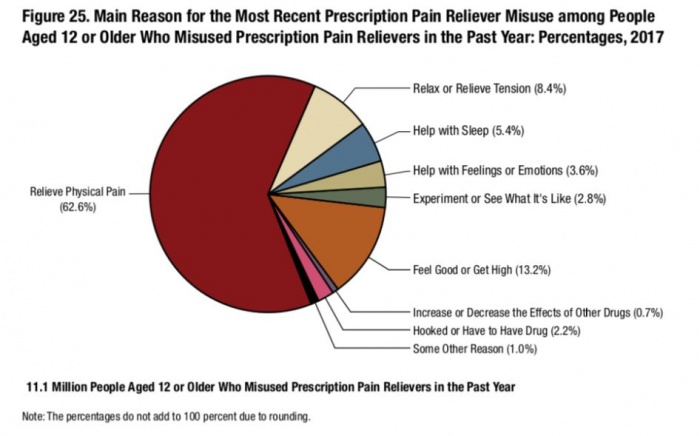
The survey also examined why people were misusing prescription pain medication.
Source of Graphic: LegitScript
It would be helpful to have (or find) better research on this, but given that this poll showed that 62.6% of the people who misused prescription pain relievers claimed to have done so for pain[2], it would seem plausible that the person giving them their own prescription pain relievers were trying to help them deal with the pain, not trying to help them get high or feed an addiction to aviod withdrawal symptoms.
This data would suggest to important strategy issues:
- It is not enough to lock up pain medications to avoid diversion. If people are givng them to friends or relatives or if they are selling them, that person would not be stopped by a typical locked box. They already know how to open that.
- A strategy to reduce prescription drug misuse should include a strong emphasis on educating people to not give or sell their medications to anyone else. This might include educating people on how they can best respond when a friend or relative approaches them to get prescription pain medication to help them address their pain problem.
- A strategy should emphasize prompt disposal of pain medications after their prescribed use is no longer needed. If people quickly dispose of their presecription pain medications when they are not necessary, they would be less likely in a situation where a friend or relative who was struggling with pain (or perhaps pretending to struggle with pain or who was struggling with paid related to withdrawal) would be able to pursuade the person to give them or sell them the drugs.
- People who might be approached by friends and relatives who are seeking access to pain medications (the #1 source based on the NSDUH) should become important actors in a strategy that emphasizes helping people before their brains have been changed due to ongoing use or misuse of opioids. A good strategy would equip these people with ways to help their friends and relatives with both physical pain and with ways to get help for other factors that may be driving misuse of opioids.
It is Getting Harder for Teens to Access Prescription Opioids
The 2017 Monitoring the Future survey of 8th, 10th and 12th graders shows encouraging news. it's getting harder for teens to access prescription opioids. Only 35.8 percent of 12th graders said they were easily available in the 2017 survey, compared to more than 54 percent in 2010[3] Overall, 43,703 students from 360 public and private schools participated in this year's MTF survey.[4]
Tools and Resources
Solutions and Tools focused on this objective.
Promising Practices and Case Studies
Examples from communities that have implemented tools focused on this objective
Scorecard Building
Potential Objective Details
Potential Measures and Data Sources
Actions to Take
Resources to Investigate
More RTI on Reducing Access to Opioids
Sources
- ^ https://www.legitscript.com/blog/2018/09/nsduh-report-opioid-abuse/
- ^ https://www.legitscript.com/blog/2018/09/nsduh-report-opioid-abuse/
- ^ https://www.drugabuse.gov/news-events/news-releases/2017/12/vaping-popular-among-teens-opioid-misuse-historic-lows
- ^ https://www.drugabuse.gov/news-events/news-releases/2017/12/vaping-popular-among-teens-opioid-misuse-historic-lows